Exchange rates, the comparison of the relative values of currencies for foreign exchange, are rarely thought of by individuals outside of special occasions like foreign travel. This lack of thought is because most day-to-day transactions occur in an individual’s domestic currency. However, if an individual is a foreign worker sending remittances (money sent to a recipient in a foreign nation) to their family abroad or a diplomat who is paid partially in a foreign currency, exchange rates become a much more important consideration as exchange rates can significantly impact one’s income in these situations.
Trade Weighted U.S. Dollar Index: Major Currencies, Goods (DISCONTINUED) (TWEXM) | FRED | St. Louis Fed (stlouisfed.org)
There are two ways to determine exchange rates. The first is a fixed exchange rate system based on the gold standard and later the gold-exchange standard. In these systems, the exchange rate of a currency was based on its value compared to gold or other gold standard currencies like the USD or British pound. Although this system was completely abandoned in the US by 1973, with other countries following suit, some nations like Iraq or Saudi Arabia do continue to use fixed exchange rates, which are pegged to the US dollar.
After the decline of the gold standard, a system of floating exchange rates proliferated. A floating exchange rate is more complex than a fixed exchange rate because it is affected by a multitude of factors including the comparison of the monetary and fiscal policies of two nations. Differences in interest rates, inflation, and public debt can be signs of possible changes in a nation’s policies and can significantly impact the exchange rate of a currency.
Another determiner of exchange rates is the political stability of a nation. Almost all legal tender is fiat currency, a currency backed by the government that issues coins and paper money. As a result, political stability is often a big factor in how exchange rates are determined. (an unstable government essentially equals an unstable currency).
Most changes in exchange rates occur in the foreign exchange market (Forex) itself. Nevertheless, governments can still influence exchange rates in many ways. In some nations like China, the government exerts direct control over the exchange rates of the nation’s currency. However, in most cases, governments will use methods such as changing the fed funds rate, printing money, and executing various expansionary fiscal policies in order to adjust the exchange rates of their currency.
The fed funds rate directly determines the interest rate that banks pay for borrowing money from the Federal Reserve, but it also has an impact on various other interest rates including those on bank loans and mortgages. Most importantly, the Fed funds rate can influence the value of the US dollar as well. The Fed uses a number of tools to adjust the Fed fund rate in order to control inflation and encourage employment.
Printing money in the treasury is perhaps one of the most direct methods of impacting exchange rates as it increases the amount of currency circulating in the market itself. The only downside of printing money is that a larger supply of currency often causes a decrease in the currency’s value, meaning this method only works when the goal is to devalue the currency.
The last tools governments can use are expansionary fiscal policies. While these policies often weaken the dollar, they can also increase economic growth and encourage investments in dollar-denominated assets, which often offsets the weakening of the dollar.
Just as there are many factors that can influence exchange rates, exchange rates can influence many internal and external affairs as well. Exchange rates often cause currency fluctuations which have an impact on capital flow, interest rates, merchandise trade, and more.
Capital flows are the movement of assets in and out of a country. Foreign investors often lean towards investments in countries that have a stable currency and strong government as this helps ensure that investments aren’t unduly devalued due to events like rapid changes in government. This increase in foreign investment can lead to an increased capital inflow.
Another point that is influenced by exchange rates is interest rates, as a significant factor for banks determining interest rates is the exchange rates of the currency. In such a sense, interest rates and exchange rates impact each other in a cyclical manner.
Merchandise trade is defined as the import and export of goods by a country. In general, a weaker currency makes it easier for a country’s export business to be competitive in international trade as the country’s businesses can offer cheaper prices to buyers while still making a profit. On the contrary, a strong currency can make it difficult to be competitive in trade.
A good example of the complex effects of exchange rates on merchandise trade is the very active trade relationship between the US and South Korea. While having a weaker currency can lead to a stronger export business, the depreciation of the Korean won compared to the US dollar has sparked concern among businesses in Korea. Korea’s industries are much more varied and multidirectional than the simpler “import natural resources and export manufactured goods” system in which having a weaker currency can strengthen competitive powers. As a result, the effects of exchange rates on trade have become a lot more complicated.
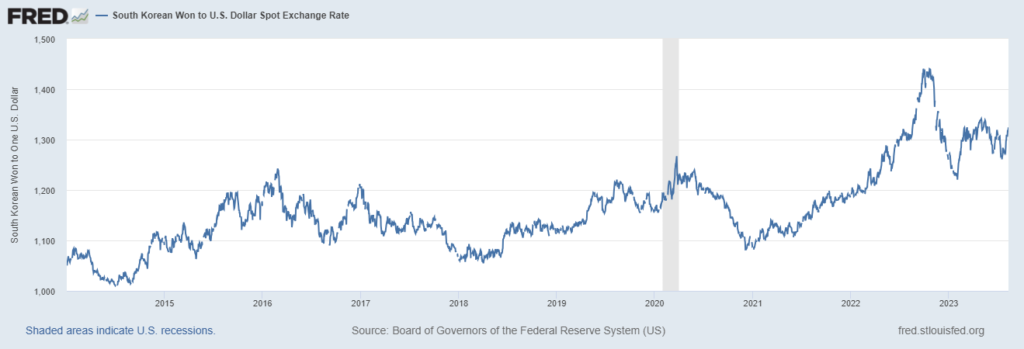
South Korean Won to U.S. Dollar Spot Exchange Rate (DEXKOUS) | FRED | St. Louis Fed (stlouisfed.org)
Furthermore, the recent changes in exchange rates are somewhat different than in the past as this time, many other currencies including the Chinese yuan, Japanese yen, and European Euro have also faced depreciation in comparison to the US dollar at the same time.
The effects of the weakened currency on Korea vary by industry. Many manufacturing industries were impacted by an increase in the already high prices of raw material imports, impacting a number of manufacturing industries. The aviation industry, which pays for aircraft rentals in USD, was also affected negatively.
On the other hand, some parts of the electronics industry saw positive changes in profits due to their main goods (semiconductors) being traded in USD. The automobile industry also benefited from increased trade competitiveness and saw an increase in exports. However, car parts manufacturers faced a far less positive situation as they had to import a lot of raw materials. Steel companies saw far less overall change as the better export situation and worse import situation balanced each other out.
Finally, content-creating businesses like gaming companies and webtoon companies (namely Kakao and Naver) saw more benefits than anything else from the rising exchange rates, likely because these industries don’t have to face import costs.
In conclusion, exchange rates can have a very complicated effect on many fields like international trade due to how multidirectional the relationships between nations and their industries can be. This can be especially impactful for nations that are highly active in international trade, such as South Korea. It is critical that nations and businesses prepare in advance for changes in exchange rates through methods such as forward contracts and financial forecasting.
References
How Does the Fed Funds Rate Work, and What Is Its Impact?
How China Influences the U.S. Dollar
How Are Exchange Rates Determined?
How Are Currency Exchange Rates Determined?
Currency Fluctuations: How they Affect the Economy
